University of Arizona TV Remote Control Study
A new study by the University of Arizona Microbiology Professor, Dr. Chuck Gerba ranks the TV remote control as holding the highest level of bacteria in a patient's hospital room. The bacteria can lead to Nosocomial Infection, or hospital-acquired infection.
Among the bacteria found, MRSA the dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria were only discovered on the remote controls. There were no traces of it on any other objects tested.
Key Objectives of the Study
- To determine the greatest number of bacteria in a patient's hospital room
- To identify THE SOURCE holding the highest level of bacteria in a patient's hospital room
- To act as a catalyst to accomplish the following
- Conduct ongoing research and studies to determine if utilizing disposable remote controls directly/indirectly decrease the level of bacteria in a patient's hospital room
- Conduct ongoing research and studies to determine if the incidence of nosocomial infections and deaths are reduced in hospitals/medical centers.
- Engage in future discussions addressing solutions to the growing number of illnesses and deaths related to nosocomial infections.
Methodology
The Study was conducted in June, July and August 2005. The study involved 15 hospital rooms to determine if the greatest number of bacteria in a patient's room occurs on the remote control. Television remote controls were divided into three groups each with a corresponding period of time. The groups included:
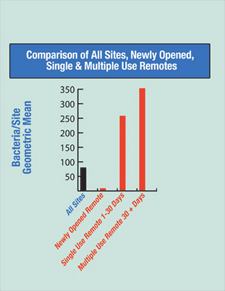
- Newly Opened Disposable Remotes - 0 Days
- Single Use Remotes - 1-30 Days
- Multiple Use Remotes - 30+ Days
- Samples were tested for total bacteria numbers, and of the 28 remotes, 20 had been used by multiple patients and 8 remotes were single patient use. The second phase involved 20 samples of newly opened disposable remotes
- Note: Each remote was tested after the patient was released and the patient room was cleaned.
Study Results
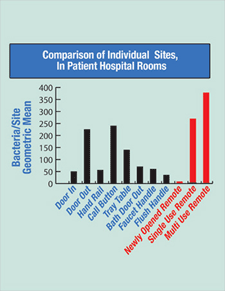
- The average total bacteria on the remote controls was 320.
- The average total bacteria on sites in the hospital room was 91.
- The average total bacteria on newly opened disposable remotes was 8.35. There was no detection of Staphylococcus Aureus on newly opened disposable remotes.
- MRSA bacteria were present on television remote controls in patient hospital rooms.
Study Sites Tested
- Television Remote Control
- Bathroom Door
- Toilet Bowl Flush Handle
- Faucet Handle
- Hand Rail
- Call Button
- Tray Table
- Door Knob
Staggering Statistics
Nosocomial Infection - Hospital-Acquired Infections
- More than 2 million Americans acquire hospital-related infections each year.
- Almost 90,000 deaths are reported each year due to nosocomial infections.
- Patients with Staph infections spend an average of 14 days in the hospital compared to other patients.
- Each year, patients with hospital-acquired infections increase hospital bills by more than $9.5 billion
